IISER Bhopal Streamlines Chemical Tagging for Drug Development
Share

Indian Institute of Science Education and Research Bhopal (IISER Bhopal) Researchers have developed a technology named ‘BHoPAL’ for attaching chemical tags to proteins, an important process in the development of drugs. Through this technology, necessary chemical moieties can be linked to specific sites of a protein without harming the protein’s efficacy.
This process is essential for two main purposes:
- Attaching proteins to fluorescent chemical tags for their visualization inside cells enabling studies focused on understanding how they perform cellular functions.
- Linking drugs to antibody proteins for selective drug delivery to diseased cells such as cancerous cells preventing undesirable side-effects of these drugs.
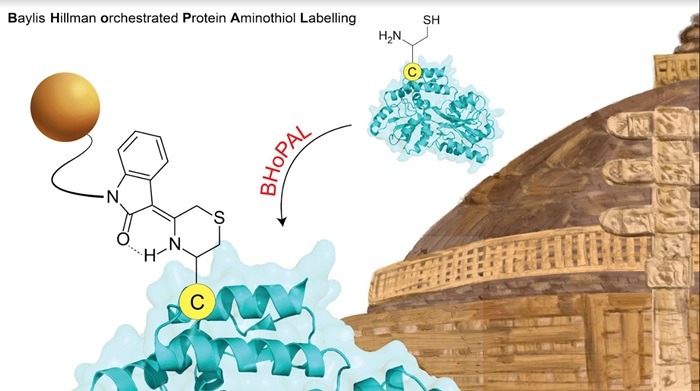
Proteins are extremely prone to loss of function when treated with chemical reagents. However, for the first time, IISER Bhopal’s novel technique eliminates this problem. This technology is called ‘Baylis Hillman orchestrated Protein Aminothiol Labelling’ (BHoPAL) which efficiently tags chemicals to proteins without compromising their function.
The research was led by Dr. Dimpy Kalia, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, IISER Bhopal who supervised her PhD students, Mudassar H Mir, Sangeeta Parmar, and Chhaya Singh on this project. Their findings have been published in the reputed, peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45124-2).
Elaborating on the objectives of this research, Dr. Dimpy Kalia, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, IISER Bhopal, said, “Proteins are cellular entities that play crucial roles in all cellular functions. Protein dysfunction results in major life-threatening diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, etc. Hence, developing effective approaches to study proteins in cells is crucial for developing therapeutic approaches targeting them.”
To test this platform, the researchers developed a new chemical reaction that has never been explored before. This reaction occurs between N-Cysteine, an important amino acid present in proteins, and Baylis Hillman adducts, and results in the formation of a linkage (a bis-heterocyclic scaffold) on specific sites on the protein. Labelling multiple sites of a protein is extremely difficult, but by using this approach, researchers can easily accomplish this task within a few minutes.
Elaborating further, Dr. Dimpy Kalia said, “What we have developed has diverse applications in chemical biology, synthetic chemistry, and medicinal chemistry. Protein conjugates fabricated using our BHoPAL technology shall be employed for the fabrication of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy. Moreover, the BHoPAL technology shall also contribute tremendously to basic biological research by enabling the imaging of proteins within human cells.”
What stands out is that this technology easily allows chemical agents to be attached to any site of the protein, a process that was very difficult to achieve before. This is a promising development that shall find applications in disease diagnosis, cellular imaging, drug development, and understanding drug-target interactions on a molecular level.












